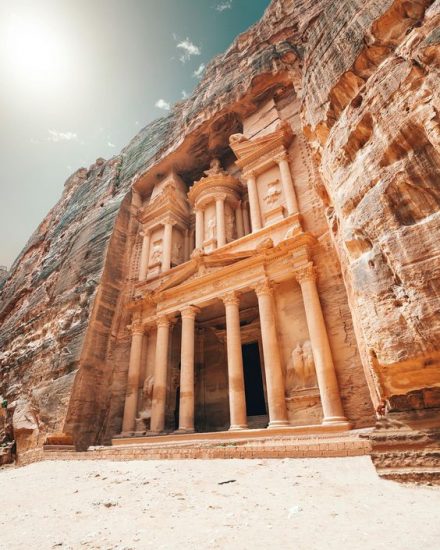
Monolithic design
Cast, carved, or excavated from a single piece of solid material most commonly from stone. The most unembellished form of monolithic architecture is a rock-cut structure, such as the monolithic churches of Ethiopia built by the Zagwe dynasty, or Petra in Jordan. Though non-modular design can often be difficult to customise and repair, designs can be unique and imaginative in both their vision and execution.

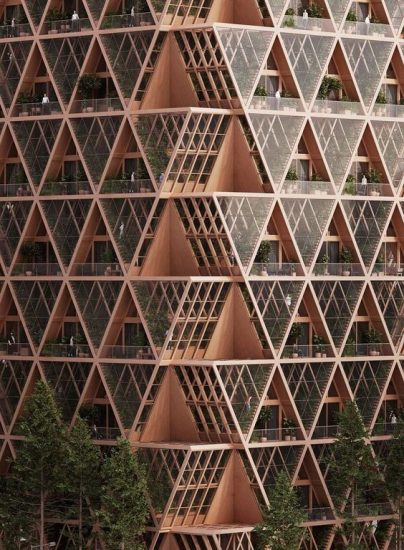
 Modular design
You can design and build a whole building using modular principles, by focusing on the single structural units that come together to create the whole building.
Modular design should be scalable, adaptable, and rigorous in its use of well-defined, modular interfaces, allowing for manufacture off site and simple assembly on site.
Modularity in platform systems is often integrated at design stage and can be used to both reduce time and cost; this is often achieved by automating processes. Software such as BIM has shown how automating scheduling as the design is being developed can allow for multiple variants of the same design to be quickly and accurately costed; providing both the client and designer direct and more meaningful data from their designs.
Modular design has the benefit of being sustainable often enabling parts of a system to be removed, reuse or upgraded, increasing the lifecycle of the system.
Compared to traditional building methods, manufacture offsite for assembly on site often requires less energy and is more energy efficient. Manufacturing platforms, CAD, CAM and machinery operation require designers and operators to efficiently plan material use, fabrication and assembly processes. This substantially reduces waste, increases productivity, accuracy, and quality.
Modular design
You can design and build a whole building using modular principles, by focusing on the single structural units that come together to create the whole building.
Modular design should be scalable, adaptable, and rigorous in its use of well-defined, modular interfaces, allowing for manufacture off site and simple assembly on site.
Modularity in platform systems is often integrated at design stage and can be used to both reduce time and cost; this is often achieved by automating processes. Software such as BIM has shown how automating scheduling as the design is being developed can allow for multiple variants of the same design to be quickly and accurately costed; providing both the client and designer direct and more meaningful data from their designs.
Modular design has the benefit of being sustainable often enabling parts of a system to be removed, reuse or upgraded, increasing the lifecycle of the system.
Compared to traditional building methods, manufacture offsite for assembly on site often requires less energy and is more energy efficient. Manufacturing platforms, CAD, CAM and machinery operation require designers and operators to efficiently plan material use, fabrication and assembly processes. This substantially reduces waste, increases productivity, accuracy, and quality.

 Different Types of Modularity
As children, most of us played with Legos or building blocks; not actually realising that at that moment, we were already designing. This is an example of a simple modular system inspiring creativity. The concept of modular design is that it utilises separate standard units and repetitive elements that can be configured in a variety of ways and easily changed. There are four different types of modular design.
Fractal Modularity
New pieces can be made for unique sets that can fit into any other set that already exists. Every piece is a module, and every set is a system. Every system can become part of another larger system, which itself is a module. Each module binds in the same way allowing for universal interchangeability.
Different Types of Modularity
As children, most of us played with Legos or building blocks; not actually realising that at that moment, we were already designing. This is an example of a simple modular system inspiring creativity. The concept of modular design is that it utilises separate standard units and repetitive elements that can be configured in a variety of ways and easily changed. There are four different types of modular design.
Fractal Modularity
New pieces can be made for unique sets that can fit into any other set that already exists. Every piece is a module, and every set is a system. Every system can become part of another larger system, which itself is a module. Each module binds in the same way allowing for universal interchangeability.
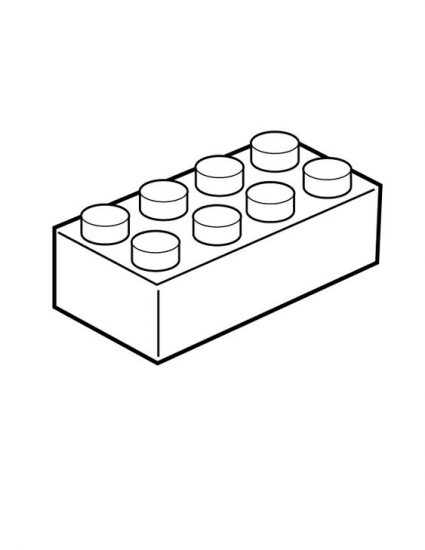 Slot Modularity
Slot modularity is when pieces cannot be universally exchanged, but there is a common base holding everything together. Each module can only be exchanged for a module of the same type.
Slot Modularity
Slot modularity is when pieces cannot be universally exchanged, but there is a common base holding everything together. Each module can only be exchanged for a module of the same type.
 Bus Modularity
The way the modules bind is identical and therefore interchangeable. A universal interface but with limited variance between modules.
Bus Modularity
The way the modules bind is identical and therefore interchangeable. A universal interface but with limited variance between modules.
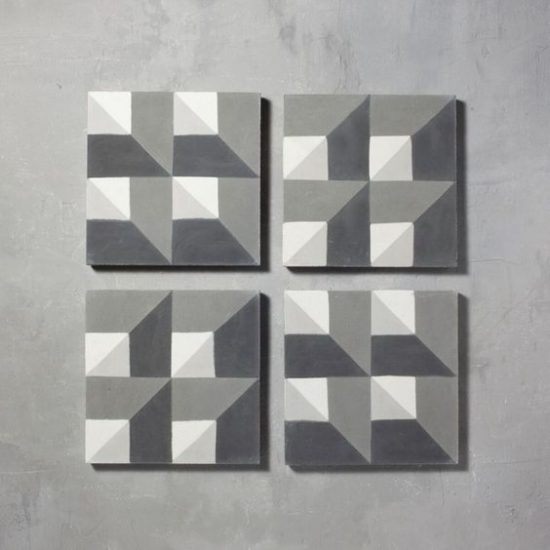 Sectional Modularity
Sectional modularity allows for infinite flexibility of infinite modules and infinite connection options. A configuration feature allows you to choose a modules size, colour and shape. Each module and interface can be unique.
Sectional Modularity
Sectional modularity allows for infinite flexibility of infinite modules and infinite connection options. A configuration feature allows you to choose a modules size, colour and shape. Each module and interface can be unique.

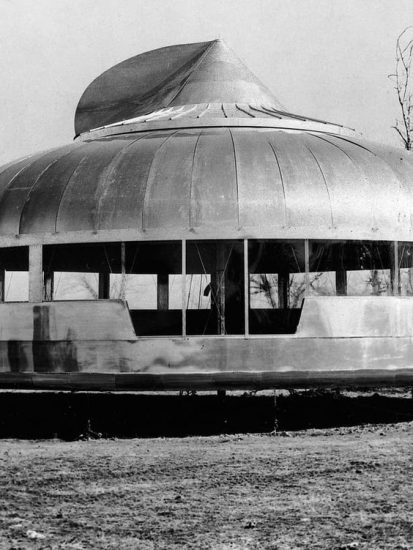
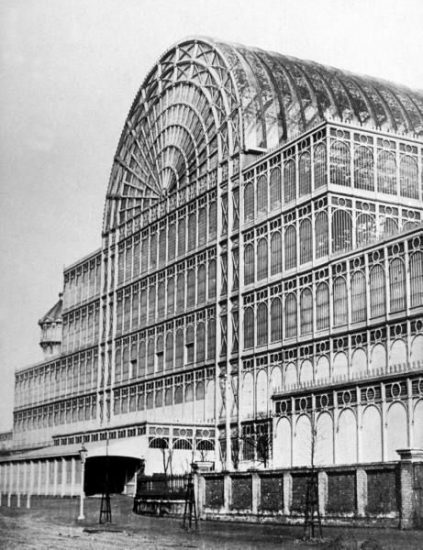
 How Modular design began
The Crystal Palace, designed in 1851 for Britain’s Great Exhibition, was one of the first examples of prefabricated design. The earliest example of modularisation was introduced by American Architect Buckminster Fuller. Fuller’s Dymaxion house featured a central space where the amenities were housed, with six modular systems fixed around it. These six identical modules were designed so that users could use each space they wanted.
How Modular design began
The Crystal Palace, designed in 1851 for Britain’s Great Exhibition, was one of the first examples of prefabricated design. The earliest example of modularisation was introduced by American Architect Buckminster Fuller. Fuller’s Dymaxion house featured a central space where the amenities were housed, with six modular systems fixed around it. These six identical modules were designed so that users could use each space they wanted.


 Another example of modular design is The Two Towers of 101 George Street in London. These residential apartment towers stand at 135m high and are constructed from over 500 modules. The construction was completed in just 35 weeks half the time it takes to build a traditional sky- scraper.
Another example of modular design is The Two Towers of 101 George Street in London. These residential apartment towers stand at 135m high and are constructed from over 500 modules. The construction was completed in just 35 weeks half the time it takes to build a traditional sky- scraper.
 How Modular design is incorporated in today’s day
The MINIMA House by Mima Architects is a modular system that allows for the interior and exterior walls of the prefabricated house to be easily moved by the user.
How Modular design is incorporated in today’s day
The MINIMA House by Mima Architects is a modular system that allows for the interior and exterior walls of the prefabricated house to be easily moved by the user.
 Space of Mind modular cabin design by Studio Puisto is an adaptable and flexible prefabricated cabin that can be used as anything the user desires and can be built anywhere in the world.
Space of Mind modular cabin design by Studio Puisto is an adaptable and flexible prefabricated cabin that can be used as anything the user desires and can be built anywhere in the world.
 The prefabricated modular library by Dot architects in China was built in 7 days utilising an open-source system developed by the Wikihouse foundation, which provides blueprints for simple structures that can be constructed quickly and simply. The Wikihouse system developed by Arhitects00 and has been used by Architects Hawkins/Brown to build 21 modular workspaces on the former Olympic Broadcast Centre in London. Manufactured offsite into individual components and assembled on site. It is versatile, configurable, enables standardisation, and allows for easier manufacture and construction.
The prefabricated modular library by Dot architects in China was built in 7 days utilising an open-source system developed by the Wikihouse foundation, which provides blueprints for simple structures that can be constructed quickly and simply. The Wikihouse system developed by Arhitects00 and has been used by Architects Hawkins/Brown to build 21 modular workspaces on the former Olympic Broadcast Centre in London. Manufactured offsite into individual components and assembled on site. It is versatile, configurable, enables standardisation, and allows for easier manufacture and construction.

 According to the 2019 industry report from Mckinsey & Company, timelines on modular projects can be accelerated up to 50% when compared with conventional design. Modular design reduces the risk that any changes made in one element of the design will create disturbance in any other element and often utilises pre-defined configurations. Structures that can transform and grow according to the changing needs of the user are being incorporated more and more by Architects, Engineers, and Manufacturers. With the growing demand for increasingly flexible and dynamic design The Splash Lab uses the concept of monolithic, modular structures to cast our basins and create flexible and functional systems that adapt to the needs of any washroom design. We design and produce commercial washroom products and modular bathroom systems that are the future of design.
According to the 2019 industry report from Mckinsey & Company, timelines on modular projects can be accelerated up to 50% when compared with conventional design. Modular design reduces the risk that any changes made in one element of the design will create disturbance in any other element and often utilises pre-defined configurations. Structures that can transform and grow according to the changing needs of the user are being incorporated more and more by Architects, Engineers, and Manufacturers. With the growing demand for increasingly flexible and dynamic design The Splash Lab uses the concept of monolithic, modular structures to cast our basins and create flexible and functional systems that adapt to the needs of any washroom design. We design and produce commercial washroom products and modular bathroom systems that are the future of design.

 Modular design
You can design and build a whole building using modular principles, by focusing on the single structural units that come together to create the whole building.
Modular design should be scalable, adaptable, and rigorous in its use of well-defined, modular interfaces, allowing for manufacture off site and simple assembly on site.
Modularity in platform systems is often integrated at design stage and can be used to both reduce time and cost; this is often achieved by automating processes. Software such as BIM has shown how automating scheduling as the design is being developed can allow for multiple variants of the same design to be quickly and accurately costed; providing both the client and designer direct and more meaningful data from their designs.
Modular design has the benefit of being sustainable often enabling parts of a system to be removed, reuse or upgraded, increasing the lifecycle of the system.
Compared to traditional building methods, manufacture offsite for assembly on site often requires less energy and is more energy efficient. Manufacturing platforms, CAD, CAM and machinery operation require designers and operators to efficiently plan material use, fabrication and assembly processes. This substantially reduces waste, increases productivity, accuracy, and quality.
Modular design
You can design and build a whole building using modular principles, by focusing on the single structural units that come together to create the whole building.
Modular design should be scalable, adaptable, and rigorous in its use of well-defined, modular interfaces, allowing for manufacture off site and simple assembly on site.
Modularity in platform systems is often integrated at design stage and can be used to both reduce time and cost; this is often achieved by automating processes. Software such as BIM has shown how automating scheduling as the design is being developed can allow for multiple variants of the same design to be quickly and accurately costed; providing both the client and designer direct and more meaningful data from their designs.
Modular design has the benefit of being sustainable often enabling parts of a system to be removed, reuse or upgraded, increasing the lifecycle of the system.
Compared to traditional building methods, manufacture offsite for assembly on site often requires less energy and is more energy efficient. Manufacturing platforms, CAD, CAM and machinery operation require designers and operators to efficiently plan material use, fabrication and assembly processes. This substantially reduces waste, increases productivity, accuracy, and quality.

 Different Types of Modularity
As children, most of us played with Legos or building blocks; not actually realising that at that moment, we were already designing. This is an example of a simple modular system inspiring creativity. The concept of modular design is that it utilises separate standard units and repetitive elements that can be configured in a variety of ways and easily changed. There are four different types of modular design.
Fractal Modularity
New pieces can be made for unique sets that can fit into any other set that already exists. Every piece is a module, and every set is a system. Every system can become part of another larger system, which itself is a module. Each module binds in the same way allowing for universal interchangeability.
Different Types of Modularity
As children, most of us played with Legos or building blocks; not actually realising that at that moment, we were already designing. This is an example of a simple modular system inspiring creativity. The concept of modular design is that it utilises separate standard units and repetitive elements that can be configured in a variety of ways and easily changed. There are four different types of modular design.
Fractal Modularity
New pieces can be made for unique sets that can fit into any other set that already exists. Every piece is a module, and every set is a system. Every system can become part of another larger system, which itself is a module. Each module binds in the same way allowing for universal interchangeability.
 Slot Modularity
Slot modularity is when pieces cannot be universally exchanged, but there is a common base holding everything together. Each module can only be exchanged for a module of the same type.
Slot Modularity
Slot modularity is when pieces cannot be universally exchanged, but there is a common base holding everything together. Each module can only be exchanged for a module of the same type.
 Bus Modularity
The way the modules bind is identical and therefore interchangeable. A universal interface but with limited variance between modules.
Bus Modularity
The way the modules bind is identical and therefore interchangeable. A universal interface but with limited variance between modules.
 Sectional Modularity
Sectional modularity allows for infinite flexibility of infinite modules and infinite connection options. A configuration feature allows you to choose a modules size, colour and shape. Each module and interface can be unique.
Sectional Modularity
Sectional modularity allows for infinite flexibility of infinite modules and infinite connection options. A configuration feature allows you to choose a modules size, colour and shape. Each module and interface can be unique.

 How Modular design began
The Crystal Palace, designed in 1851 for Britain’s Great Exhibition, was one of the first examples of prefabricated design. The earliest example of modularisation was introduced by American Architect Buckminster Fuller. Fuller’s Dymaxion house featured a central space where the amenities were housed, with six modular systems fixed around it. These six identical modules were designed so that users could use each space they wanted.
How Modular design began
The Crystal Palace, designed in 1851 for Britain’s Great Exhibition, was one of the first examples of prefabricated design. The earliest example of modularisation was introduced by American Architect Buckminster Fuller. Fuller’s Dymaxion house featured a central space where the amenities were housed, with six modular systems fixed around it. These six identical modules were designed so that users could use each space they wanted.


 Another example of modular design is The Two Towers of 101 George Street in London. These residential apartment towers stand at 135m high and are constructed from over 500 modules. The construction was completed in just 35 weeks half the time it takes to build a traditional sky- scraper.
Another example of modular design is The Two Towers of 101 George Street in London. These residential apartment towers stand at 135m high and are constructed from over 500 modules. The construction was completed in just 35 weeks half the time it takes to build a traditional sky- scraper.
 How Modular design is incorporated in today’s day
The MINIMA House by Mima Architects is a modular system that allows for the interior and exterior walls of the prefabricated house to be easily moved by the user.
How Modular design is incorporated in today’s day
The MINIMA House by Mima Architects is a modular system that allows for the interior and exterior walls of the prefabricated house to be easily moved by the user.
 Space of Mind modular cabin design by Studio Puisto is an adaptable and flexible prefabricated cabin that can be used as anything the user desires and can be built anywhere in the world.
Space of Mind modular cabin design by Studio Puisto is an adaptable and flexible prefabricated cabin that can be used as anything the user desires and can be built anywhere in the world.
 The prefabricated modular library by Dot architects in China was built in 7 days utilising an open-source system developed by the Wikihouse foundation, which provides blueprints for simple structures that can be constructed quickly and simply. The Wikihouse system developed by Arhitects00 and has been used by Architects Hawkins/Brown to build 21 modular workspaces on the former Olympic Broadcast Centre in London. Manufactured offsite into individual components and assembled on site. It is versatile, configurable, enables standardisation, and allows for easier manufacture and construction.
The prefabricated modular library by Dot architects in China was built in 7 days utilising an open-source system developed by the Wikihouse foundation, which provides blueprints for simple structures that can be constructed quickly and simply. The Wikihouse system developed by Arhitects00 and has been used by Architects Hawkins/Brown to build 21 modular workspaces on the former Olympic Broadcast Centre in London. Manufactured offsite into individual components and assembled on site. It is versatile, configurable, enables standardisation, and allows for easier manufacture and construction.

 According to the 2019 industry report from Mckinsey & Company, timelines on modular projects can be accelerated up to 50% when compared with conventional design. Modular design reduces the risk that any changes made in one element of the design will create disturbance in any other element and often utilises pre-defined configurations. Structures that can transform and grow according to the changing needs of the user are being incorporated more and more by Architects, Engineers, and Manufacturers. With the growing demand for increasingly flexible and dynamic design The Splash Lab uses the concept of monolithic, modular structures to cast our basins and create flexible and functional systems that adapt to the needs of any washroom design. We design and produce commercial washroom products and modular bathroom systems that are the future of design.
According to the 2019 industry report from Mckinsey & Company, timelines on modular projects can be accelerated up to 50% when compared with conventional design. Modular design reduces the risk that any changes made in one element of the design will create disturbance in any other element and often utilises pre-defined configurations. Structures that can transform and grow according to the changing needs of the user are being incorporated more and more by Architects, Engineers, and Manufacturers. With the growing demand for increasingly flexible and dynamic design The Splash Lab uses the concept of monolithic, modular structures to cast our basins and create flexible and functional systems that adapt to the needs of any washroom design. We design and produce commercial washroom products and modular bathroom systems that are the future of design.